
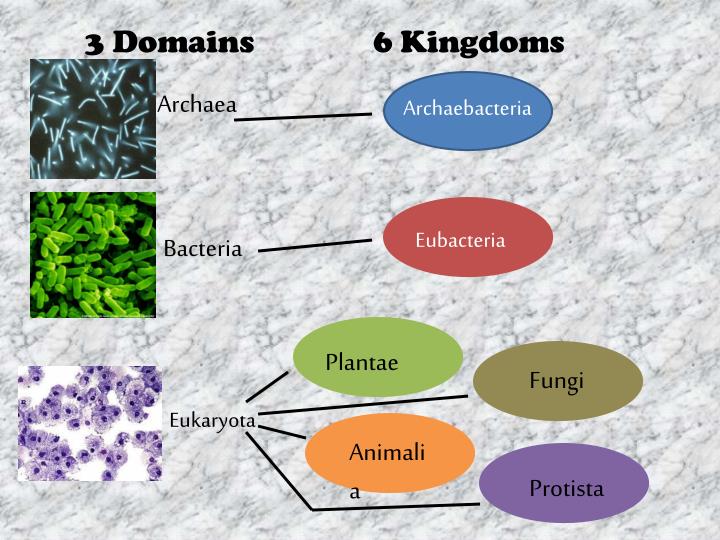
Within the domain Eukarya, there are four kingdoms: Protista, Fungi, Plantae, and Animalia. The domain Eukarya includes all organisms that have DNA contained within a nucleus. Image courtesy of Jörg Hempel, Wikimedia Commons Some species may look very similar to each other, so it is important for scientists to establish specific criteria for what distinguishes one species from another. They are also interested in studying the evolutionary mechanisms that generate and maintain new species. Scientists are interested in classifying the many species currently living on Earth, as well as those that are no longer living.
The relationships between all of these different extant and extinct organisms on our planet are amazingly intricate and complex. There is an extensive fossil record of plants and animals that lived in the past and that may be distant relatives of living species. This fact supports the idea that humans share a closer common ancestor to apes than dogs.Īlthough scientists have described nearly 2 million species on Earth, this number is estimated to only be a small proportion of the actual number of species alive today. Humans and apes share functional similarity in hands and facial features when compared to a dog’s face and paws. Human beings are mammals and are more closely related to primates, such as apes, than to other mammals such as dogs. Taxonomy takes into account the functional similarity as well as genetic similarity of individuals. Your cousins are not as closely related to you because your common ancestor is farther away-a grandparent (your parent’s parent). Your closest relatives would be siblings (brothers and sisters) because you share the closest common ancestor-a parent. The more recent the ancestor, the more closely related the organisms are. When two organisms are related, it means that they share a common ancestor. Your biological relatives include those that you are related to by birth, for example parents, brothers, sisters, cousins, aunts, uncles, and grandparents. Think about your own biological relatives. Organisms are classified based upon their similarities and differences. Taxonomy is the study of relationships between living things and the formal classification of organisms into groups based upon those hypothesized relationships. One branch of biology, called taxonomy, focuses on the classification of living things. Think about some of the things classified around your home or school and the methods used to classify non-living things. One way that we try to accomplish this is by classifying things into different groups based on how things are alike and different. Humans constantly try to organize information about the world around them in meaningful ways.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
